

Learn about star patterns, orbits, and galaxies with this solar system flash cards.
There are 30 flash cards in this set (5 pages to print.)
To use:
1. Print out the cards.
2. Cut along the dashed lines.
3. Fold along the solid lines.
Sample flash cards in this set:
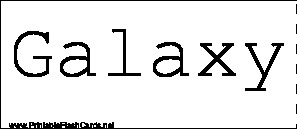



| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
| Galaxy | A star system containing millions to billions of stars, held together by their own gravity. |
| Star | A sphere of mostly hydrogen and helium gas that is held together by its own gravity and has enough energy to illuminate itself (produce its own light) |
| Planet | A large body (object) in space that moves around a star. |
| Moon | A small rounded body (object) that orbits a planet. |
| Astronomical Unit (AU) | The distance between the earth and the sun, (93 million mile) = 1 AU |
| Helocentric | A theory based on the idea that the Sun is the center of our solar system and the planets orbit the sun. |
| Geocentric | A theory that believed the earth was the center of our solar system. |
| Galileo | A scientist that constructed a telescope and supported Copernicus' theory, which stated we have a sun-centered solar system. |
| Copernicus | The first scientist to propose that the sun was the center of our solar system. |
| Orbit | To revolve (move) in a set path is space around another object because of gravity. |
| Gravity | A force of attraction between two objects that tries to pull them towards each other. Anything with mass has gravitational pull. |
| Inertia | The tendency of an object to remain still or continue to move in a constant direction at a constant speed unless another force changes its speed or direction. |
| Rotation | Spinning motion of a body about its axis. Earths rotation causes day and night. |
| Revolution | Orbital motion of one body about another, such as the earth around the sun. |
| Axis | An imaginary line that stretches from pole to pole through the interior of a planet, around which the planet rotations. |
| Waxing | When the amount of the sunlit portion of the near side of the moon that we see appears to get bigger. |
| Waning | When the amount of the sunlit portion of the near side of the moon that we see appears to get smaller. |
| Gibbous Moon | The phase of the moon when more than half of the Moon's near side is sunlit. |
| Crescent Moon | The phase of the moon when a thin part of the moon's near side is sunlit. |
| Quarter Moon | The phase of the moon when half of the Moon's near side is sunlit. |
| Full Moon | The phase of the moon when all of the Moon's near side is sunlit. |
| New Moon | The phase of the moon when the Moon's near side receives NO sunlight. |
| Solar eclipse | When the new moon passes directly between the earth and the sun, temporarily blocking the sun's light. |
| Lunar eclipse | When the moon passes through the shadow of Earth, temporarily blocking the moon from illuminating the light of the sun causing a darkening of its surface. |
| Season | Pattern of temperature changes and other weather trends over the course of a year. Earth's tilted axis and orbit cause our seasons. |
| Indirect rays | When the angle of the sun's light is spread out over a large area. |
| Direct rays | When the sun's light is concentrated on a small area. |
| Tide | The periodic rising and falling of the water level of the ocean, caused by the gravity of the moon and the sun. |
| Low Tide | Between the two bulges of ocean water there are dips in the level of water, these are low tides. Most places experience two high and two low tides each day. |
| High Tide | When the moon's gravity pulls the most strongly on the side of the Earth facing the moon (the side in line with the moon), the Earth's water bulges on this side as a direct high tide, and on the opposite side of the earth as an indirect high tide. |