
Learn the ways in which dairy products are made, pasteurized or spoiled in these food flash cards
There are 13 flash cards in this set (4 pages to print.)
To use:
1. Print out the cards.
2. Cut along the dashed lines.
3. Fold along the solid lines.
Sample flash cards in this set:




| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
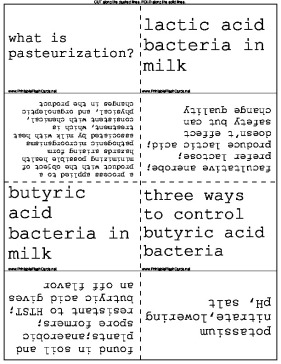
| what is pasteurization? | a process applied to a product with the object of minimizing possible health hazards arising form pathogenic microorganisms associated by milk with heat treatment, which is consistent with chemical, physical, and organoleptic changes in the product |
| lactic acid bacteria in milk | facultative anerobe; prefer lactose; produce lactic acid; doesn't effect safety but can change quality |
| butyric acid bacteria in milk | found in soil and plants;anaerobic spore formers; resistant to HTST; butryic acid gives an off flavor |
| three ways to control butyric acid bacteria | potassium nitrate,lowering pH, salt |
| Coli bacteria in milk | faculative anaerobes;related mastitis; produce lactic acid, CO2, hydrogen peroxide; results in bitter unclean taste; generally controlled by HTST |
| putrefaction bacteria in milk | both anaerobe and anaerobic; contain proteases that break down protein to ammonia; contain lipases; yields poor quality butter and cheese |
| what happens with low pH in milk? | precipitation of curds; thickening increases viscosity; yogurt; buttermilk; cheese ripening |
| starter cultures | streptococcus lactis-initator, produces proteases, if its casein will start precipitation of curd can start at pH 7.2 ends at about 6.2 |
| what continues after streptococcus lactis cant grow anymore | lactobacillus casei continue to grow at pH six and below |
| oxidative rancidity | oxidation of double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids; metallic flavor |
| hydrolytic rancidity | free fatty acids are split from the glycerol in triglycerides; activated by a lipase heat or agitation; pasteurization in activates lipases |
| homogenization | avoiding separation of fat content; milk is pressed through screens with tiny apertures 2500 psi; makes fat molecules the same size; |
| effects of homogenization | protein layers form around fat globules; increased viscosity; whiter appearance; less stable to heat and light; more sensitive to oxidative rancidity; curds are softer; less distinctive milk flavor |